OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL (OIG)
(CT:ORG-706; 08-15-2025)
(Office of Origin: OIG)
1 FAM 051 OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL (OIG)
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Office of Inspector General (OIG) was created by the Congress to:
(1) Conduct and supervise independent and objective audits, inspections, evaluations, reviews, and investigations of the programs and operations of the Department of State (Department), the U.S. Agency for Global Media (USAGM), the International Boundary and Water Commission, United States and Mexico, U.S. Section (USIBWC), and any other organization for which OIG is assigned oversight responsibility;
(2) Recommend corrective action and report on progress made in implementing these recommendations;
(3) Recommend actions to promote economy, efficiency, and effectiveness; and to prevent fraud and abuse in the programs and operations of the Department, the USAGM, and the USIBWC and any other organization for which OIG is assigned oversight responsibility; and
(4) Keep the Secretary of State (Secretary), the Chief Executive Officer of USAGM (CEO), the United States Commissioner (Commissioner) of USIBWC, the head(s) of any other organization(s) for which OIG is assigned oversight responsibility, and the Congress fully and currently informed concerning fraud and other serious problems, abuses, and deficiencies relating to the administration of each organization’s respective programs and operations.
1 FAM 051.1 Authorities
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The OIG exercises authorities under numerous statutes and executive orders, including, but not limited to:
(1) Inspector General Act of 1978, as amended (5 U.S.C. 401-424);
(2) Inspector General Empowerment Act of 2016 (5 U.S.C. app.);
(3) Securing Inspector General Independence Act of 2022 (Public Law No. 117-263, 5201-5275 (2022));
(4) Department of State Authorities Act, Fiscal Year 2017 (22 U.S.C. 2651 note);
(5) Foreign Service Act of 1980, sec. 209 (22 U.S.C. 3929);
(6) Examination of Records (48 CFR 652.215-70);
(7) Attorney General Guidelines for Offices of Inspector General with Statutory Law Enforcement Authority (December 8, 2003);
(8) The Attorney General’s Guidelines Regarding the Use of Confidential Informants (May 30, 2002);
(9) The Attorney General’s Guidelines on Federal Bureau of Investigation Undercover Operations (May 30, 2002);
(10) The Attorney General’s Guidelines for Domestic FBI Operations (September 29, 2008);
(11) Whistleblower Protection Act of 1989, as amended (5 U.S.C. 2302);
(12) Whistleblower Protection Enhancement Act of 2012;
(13) Intelligence Community Whistleblower Protection Act of 1998;
(14)Enhancement of Contractor Protection from Reprisal for Disclosure of Certain Information (41 U.S.C. 4712);
(15) Presidential Policy Directive/PPD-19, Protecting Whistleblowers with Access to Classified Information (October 10, 2012); and
(16) Memorandum of Understanding between the United States Section of the International Boundary and Water Commission, United States and Mexico, and the Department of State, sec. 2.4 (November 14, 2016).
1 FAM 051.2 Professional Standards
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
a. Section 7 of the Inspector General Reform Act of 2008 established the Council of the Inspectors General on Integrity and Efficiency (CIGIE) and requires offices of inspectors general to adhere to professional standards developed by CIGIE.
b. Pursuant to this requirement, OIG follows the professional standards published by CIGIE and the most current professional auditing standards published by the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), including:
(1) Government Auditing Standards (Yellow Book), GAO;
(2) Quality Standards for Investigations, CIGIE;
(3) Quality Standards for Inspection and Evaluation (Blue Book), CIGIE;
(4) Quality Standards for Federal Offices of Inspector General (Silver Book), CIGIE; and
(5) Quality Standards for Digital Forensics, CIGIE.
1 FAM 052 ORGANIZATION
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
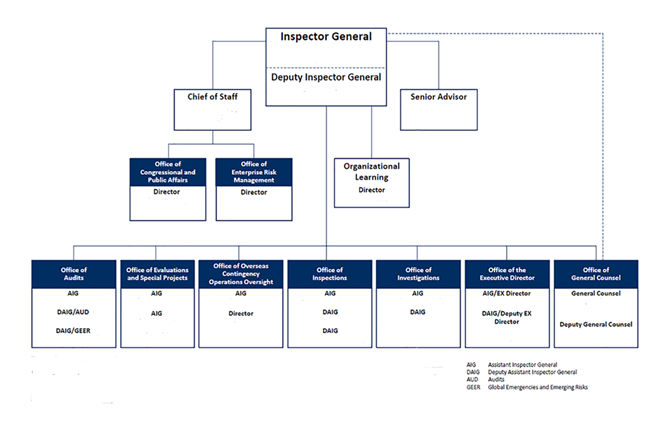
The organizational chart for OIG is available in 1 FAM Exhibit 050(2).
1 FAM 052.1 Inspector General
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
a. OIG is headed by an Inspector General nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate. Consistent with 22 U.S.C. 4861, no career member of the Foreign Service may be appointed Inspector General. The Inspector General reports directly to the Secretary, CEO, Commissioner, and the head of any other organization for which the OIG is assigned oversight responsibility.
b. The Inspector General:
(1) Periodically inspects and audits the administration of activities and operations of Foreign Service posts, bureaus, and other operating units of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which the OIG has oversight responsibility. This includes reviews of activities and operations performed under the direction, coordination, and supervision of chiefs of mission to determine whether they are being administered in accordance with U.S. foreign policy and are consistent with the responsibilities of the Secretary and chief of mission (COM).
(2) Receives and investigates complaints or information related to the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and/or any other organization for which the OIG has oversight responsibility concerning the possible existence of:
(a) Violation of laws, rules, or regulations;
(b) Mismanagement, gross waste of funds, or abuse of authority; and/or
(c) Substantial and specific danger to public health or safety.
(3) Reports expeditiously to the Attorney General whenever the Inspector General has reasonable grounds to believe there has been a violation of Federal criminal law.
(4) Reports immediately to the Secretary, CEO, Commissioner, or head of any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility instances of particularly serious or flagrant problems, abuses, or deficiencies relating to the administration of their respective programs and operations.
(5) Prepares and transmits to the Secretary, the CEO, or head of any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility when applicable, no later than April 30 and October 31 of each year, a semiannual report (SAR) to the Congress summarizing OIG activities during the preceding 6-month periods ending March 31 and September 30. Reporting requirements for the SAR are found in Section 5 of the Inspector General Act, as amended.
(6) Serves as a nonvoting member of the Department’s Management Control Steering Committee (MCSC).
(7) Has the functions, powers, and duties of an agency head or appointing authority under the following provisions under 5 U.S.C.:
(a) Subchapter II of Chapter 35;
(b) Sections 8335(b), 8336, 8344, 8414, 8468, and 8425(b); and
(c) All provisions relating to the Senior Executive Service, as determined by the Office of Personnel Management.
1 FAM 052.2 Deputy Inspector General
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
a. The Deputy Inspector General reports directly to the Inspector General.
b. The Deputy Inspector General:
(1) Pursuant to the Federal Vacancies Reform Act performs the functions and duties of the Inspector General temporarily as first assistant to the Inspector General when the Inspector General is unable to do so; and
(2) At the direction of the Inspector General, provides supervision, direction, and guidance to OIG offices as specified by the Inspector General, except the Office of General Counsel (OIG/OGC), which by statute reports directly to the Inspector General.
1 FAM 052.3 Assistant Inspectors General
1 FAM 052.3-1 Assistant Inspector General for Audits
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Assistant Inspector General for Audits heads the Office of Audits (OIG/AUD) conducts, supervises, and coordinates audits of the programs and operations of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility, as well as contractors and grantees funded by these organizations.
1 FAM 052.3-2 Assistant Inspector General for Investigations
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Assistant Inspector General for Investigations heads the Office of Investigations (OIG/INV) and conducts, supervises, and coordinates investigations of the programs and operations of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility, as well as contractors and grantees funded by these organizations.
1 FAM 052.3-3 Assistant Inspector General for Inspections
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Assistant Inspector General for Inspections heads the Office of Inspections (OIG/ISP) and conducts, supervises, and coordinates inspections of the programs and operations of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility, as well as contractors and grantees funded by these organizations.
1 FAM 052.3-4 Assistant Inspector General for Evaluations and Special Projects
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Assistant Inspector General for Evaluations and Special Projects heads the Office of Evaluations and Special Projects (OIG/ESP) and conducts, supervises, and coordinates evaluations and special reviews related to issues of significant public or congressional concern, as well as systemic and recurring management challenges at the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility. ESP is also responsible for investigating allegations of whistleblower retaliation and allegations of administrative misconduct by senior officials. The Assistant Inspector General for ESP also serves as the Whistleblower Protection Coordinator. The Whistleblower Protection Coordinator educates employees of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility, including those of their respective contractors and grantees, about prohibitions on retaliation for protected disclosures and advise individuals who have made or are contemplating making a protected disclosure about the rights and remedies against retaliation for protected disclosures. The Whistleblower Protection Coordinator is prohibited from acting as a legal representative, agent, or advocate of the employee or former employee.
1 FAM 052.3-5 Assistant Inspector General for Management and Executive Director
(CT:ORG-697; 03-17-2025)
The Assistant Inspector General for Management/Executive Director heads the Office of Management/the Executive Director (OIG/EX) and is responsible for human resources; in OIG hiring practices; training; procurement; administrative and general services; budget, finance, and travel; information technology support for OIG; management of OIG’s security program; and maintaining and analyzing the database for OIG reports, findings, and recommendations. The Executive Director also serves as the OIG’s Management Control Coordinator (MCC).
1 FAM 052.3-6 Assistant Inspector General for Overseas Contingency Operations
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Assistant Inspector General for Overseas Contingency Operations heads the Office of Overseas Contingency Operations (OIG/OCO). OIG/OCO, as part of the Lead Inspector General (Lead IG) framework established by Section 8L of the Inspector General Act with the Department of Defense (DoD) IG and the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) IG, contributes to Lead IG quarterly reports on each overseas contingency operation (OCO) and to interagency Lead IG planning for effective oversight of the whole of government effort associated with each OCO. In executing OIG’s Lead IG responsibilities jointly with DoD IG and USAID IG, OIG/OCO coordinates regularly with OIG’s other program offices and with Department bureaus, offices, and posts on OCO-related issues.
1 FAM 052.4 General Counsel to the Inspector General (OIG/OGC)
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
a. To maintain and ensure its independence, pursuant to the Inspector General Act of 1978, section 3(g), OIG has its own General Counsel, who reports to and is under the direct supervision of the Inspector General. The General Counsel heads the Office of General Counsel (OIG/OGC).
b. OIG/OGC’s primary functions include:
(1) Providing legal advice, guidance and direction concerning OIG activities to the Inspector General, Deputy Inspector General, OIG senior staff, and other OIG employees (OIG staff) and advising on applicable legal and law enforcement standards regarding OIG work product;
(2) Serving as the primary point of contact on behalf of the OIG with counsel in the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibilities and serving as OIG’s liaison to the Office of the Legal Adviser;
(3) Serving as the primary point of contact and adviser on matters concerning Freedom of Information Act (FOIA), Privacy Act (PA) and other information management laws, regulations, and matters;
(4) Representing OIG in litigation and administrative hearings; and
(5) Providing guidance, review, analysis, and referral to the Designated Agency Ethics Official (DAEO), Office of Government Ethics (OGE), the Council of the Inspectors General on Integrity and Efficiency (CIGIE), or others as appropriate, for OIG staff regarding ethics-related issues, conflicts of interest, and independence issues.
1 FAM 052.5 Chief of Staff
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The OIG Chief of Staff (CoS) serves as the primary staff liaison to OIG and executive staff representing and assisting the Inspector General in fulfilling responsibilities throughout the State OIG. The CoS also provides executive direction and leadership for the OIG Office of Enterprise Risk Management (OIG/ERM), including supervising the ERM Director and overseeing ERM’s programs and staff, and the OIG’s Office of Congressional and Public Affairs (OIG/CPA), including supervising the CPA Director and overseeing CPA’s programs and staff.
1 FAM 052.5-1 Office of Congressional and Public Affairs
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Office of Congressional and Public Affairs (OIG/CPA) is led by the CPA Director. OIG/CPA is responsible for:
(1) Reviewing and tracking legislation;
(2) Overseeing preparation of congressional briefings and testimony;
(3) Responding to requests from Congress and the media;
(4) Serving as spokesperson for OIG; and
(5) Managing content and coordinating policy for OIG web sites on the Internet, intranet, and classified network, as well as social media outreach.
1 FAM 052.5-2 Office of Enterprise Risk Management
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Office of Enterprise Risk Management (OIG/ERM) is led by the ERM Director. The office is responsible for developing and managing OIG’s enterprise risk management program as well as corporate processes related to strategic planning, work planning, organizational performance management, and enterprise-wide policy.
1 FAM 053 DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
1 FAM 053.1 Authority of the Inspector General
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
a. As necessary for carrying out the duties and responsibilities provided by the Inspector General Act of 1978, as amended, the Inspector General is authorized to:
(1) Have prompt access to all records, including access to reports, audits, reviews, documents, papers, recommendations, or other material available to the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which the OIG has oversight responsibility that relate to those organizations’ programs and operations, including cables with limited, exclusive, and/or no further distribution;
(2) Conduct investigations and prepare reports relating to the administration of the programs and operations of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which the OIG has oversight responsibility that the Inspector General determines are necessary;
(3) Request any information or assistance the Inspector General determines is necessary from any Federal, State, or local governmental agency or unit thereof;
(4) Require by subpoena the production of all information, documents, reports, answers, records, accounts, papers, and other documentary evidence or data in any medium (including electronically stored information, as well as any tangible thing). Employees of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which the OIG has oversight responsibility have a duty to cooperate with OIG and no subpoena is required to obtain timely information and assistance from employees. A subpoena, in the case of contumacy or refusal to obey, shall be enforceable by order of any appropriate U.S. district court. Procedures other than subpoenas shall be used by the Inspector General to obtain documents and information from Federal agencies;
(5) Administer to or take from any person an oath, affirmation, or affidavit;
(6) Have direct and prompt access, when necessary, to the Secretary, CEO, Commissioner, and the head(s) of any other organization(s) for which the OIG has oversight responsibility;
(7) Have broad authority to structure the operation of OIG and independently recruit, select, employ, and/or appoint such officers and employees to carry out the functions, powers, and duties of OIG, subject to the provisions of Title 5, United States Code, governing appointments in the competitive service, and the provisions of chapter 51 and subchapter III of chapter 53 of such title relating to classification and General Schedule pay rates;
(8) Request that employees of the Department and members of the Foreign Service be detailed or assigned as employees of OIG. The individuals assigned and appointed shall be responsible solely to the Inspector General or designee, who shall prepare the performance evaluation reports for such individuals;
(9) Enter into contracts and other arrangements for audits, studies, analyses, and other services with executive branch agencies, State and local governments, or private organizations or persons; and
(10) Obtain services as authorized by 5 U.S.C. 3109 at daily rates not to exceed the equivalent rate prescribed for grade GS–15 of the General Schedule by 5 U.S.C. 5332.
b. Consistent with 22 U.S.C. 6209a(b), the Inspector General shall respect the journalistic integrity of USAGM broadcasters and may not evaluate the philosophical or political perspectives reflected in the content of broadcasts.
c. The Inspector General, the Assistant Inspector General for Investigations, and any special agent supervised by the Assistant Inspector General for Investigations, has been authorized by the Attorney General to:
(1) Carry a firearm while engaged in official duties, as authorized under the Inspector General Act of 1978, as amended, or other statute, or as expressly authorized by the Attorney General (if compliant with firearm training requirements);
(2) Make an arrest without a warrant while engaged in official duties as authorized under the Inspector General Act or other statute, or as expressly authorized by the Attorney General, for any offense against the United States committed in their presence that is cognizable under the laws of the United States if the Inspector General has reasonable grounds to believe that the person to be arrested has committed or is committing such offense; and
(3) Seek and execute warrants for arrest, search of a premises, and seizure of evidence issued under the authority of the United States upon probable cause to believe a violation has been committed.
1 FAM 053.2 Access and Cooperation Requirements
1 FAM 053.2-1 Secretary of State, the Chief Executive Officer of the U.S. Agency for Global Media, and the Commissioner of the International Boundary and Water Commission, United States and Mexico, U.S. Section
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Secretary, CEO, and Commissioner (or the officers next in rank) shall:
(1) Pursuant to Section 6(d) of the Inspector General Act of 1978, provide OIG with appropriate and adequate office space at headquarters buildings or domestic offices and posts abroad and necessary equipment, office supplies, communications facilities, and services, to operate the offices and provide necessary maintenance service for the offices and equipment and facilities located in the offices;
(2) Protect the confidentiality, integrity, and independence of OIG data on information systems that are managed by the Department, consistent with the Department's existing security obligations for those systems. Department staff shall not access OIG proprietary data, except as authorized by the Inspector General.
(3) Transmit reports made by the Inspector General of particularly serious or flagrant problems, abuses, or deficiencies relating to the administration of programs and operations of the Department or USAGM, along with any comments the Secretary or the CEO deem appropriate, to the appropriate committees or subcommittees of Congress within seven calendar days;
(4) Transmit the semiannual report (SAR) to the Congress, with any comments deemed appropriate, to the appropriate committees or subcommittees of the Congress within 30 days of receiving it from the Inspector General, and within 60 days of transmittal to the Congress, make copies of the reports available to the public upon request at a reasonable cost;
(5) Not assign to the Inspector General any general program operating responsibilities;
(6) Not prevent or prohibit the Inspector General from initiating, carrying out, or completing any audit, inspection, investigation, or review, or from issuing any subpoena during the course of OIG work; and
(7) Not prohibit OIG employees from obtaining the requisite national security eligibility required to perform their authorities under the IG Act. The determination of national security eligibility would be adjudicated in accordance with E.O. 12968, National Security Adjudicative Guidelines, and agency policies.
1 FAM 053.2-2 Personnel at All Levels
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
a. This section applies to all employees, locally employed staff, individuals providing services via personal service agreements, and personal service contractors of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility.
b. All such individuals are responsible for promoting honesty, integrity, effectiveness, and efficiency in the conduct of their work.
c. All such individuals shall promptly and without interference or undue inquiry, provide requested assistance and information to OIG personnel and to independent contractors working on behalf of OIG carrying out OIG’s official responsibilities. In all OIG investigative activities, OIG employees may directly contact any Department, USAGM, or USIBWC employee, contractor, or grantee. Department, USAGM, or USIBWC, contractor, or grantee staff are not required to obtain permission or inform managers before speaking with OIG representatives during investigations, audits, evaluations or other OIG reviews. However, employees may contact a manager with questions regarding their responsibility to assist and cooperate or schedule meetings with the OIG, unless, in the context of an investigation, they are instructed not to do so by OIG personnel. Under these circumstances, managers should not question staff about their interactions with the OIG. By law, all Department of State, USAGM, and USIBWC personnel are required to comply with a request for an interview or access to documents from the Office of the Inspector General (OIG) within 60 days. Such cooperation includes, but is not limited to:
(1) Providing prompt access to, and the originals of, if necessary, all records, reports, audits, reviews, documents, papers, recommendations, electronic media, or other materials available to the post, bureau, unit, or other entity that relate to programs, operations, grantees, contractors, and assignees, in any format;
(2) Allowing access to Department, USAGM, and USIBWC data in financial management or other systems and local or Bureau/Office network drives, as needed, if OIG determines that access will provide useful information or improve efficiency of its work and such access can be reasonably provided;
(3) Cooperating fully by disclosing complete and accurate information pertaining to matters under OIG investigation and review;
(4) Informing OIG personnel of any other areas or activities they believe require special attention;
(5) Not concealing information or obstructing audits, inspections, investigations, or other official OIG reviews or inquiries;
(6) Reporting known or suspected waste, fraud, abuse, violations of law, false certifications, and corruption on a timely basis to OIG/INV via the OIG Hotline (see paragraph f below);
(7) Honoring requests for interviews from OIG personnel and contractors performing work on behalf of OIG in a timely manner;
(8) Honoring OIG requests to meet individually with employees of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility and facilitating OIG requests to meet individually with employees of contractors or grantees and respecting individuals’ rights to speak directly and confidentially with OIG personnel; and
(9) Refraining from inappropriate activity, including retaliation, that might inhibit employees of the Department, USAGM, USIBWC, and any other organization for which OIG has oversight responsibility or of contractors or grantees from individual communication and cooperation with OIG personnel.
NOTE: On February 9, 2022, the Department of State amended the Department of State Acquisition Regulation (DOSAR), to add a new contract clause relating to OIG requests for examination of contractor records. 48 CFR 615 provides the policy, and 48 CFR 652.215-70 provides the clause that will be included in all solicitations and contracts, other than contracts by negotiation.
d. When any personnel described in 1 FAM 053.2-2 paragraph a believes other personnel have committed a criminal act, the individual shall promptly inform OIG of the matter and shall not, without the written authorization of an OIG official:
(1) Engage in any independent investigation or inquiry;
(2) Discuss the matter with the suspected wrongdoer or representative; or
(3) Disclose to unauthorized persons information regarding the matter or information that identifies or could reasonably lead to identifying the person(s) allegedly involved in the criminal act.
e. Contractors and grantees are required to notify OIG when they have credible evidence that a principal, employee, agent, or subcontractor of the contractor/grantee has committed a violation of the civil False Claims Act or a violation of Federal criminal law involving fraud, conflict of interest, bribery, gratuity, or trafficking in persons violations in connection with the award, performance, or closeout of a contract or grant or any related subcontract or subgrant. The individual making the report must be an officer or manager empowered to speak for the company.
f. Individuals should report information to the OIG Hotline using OIG’s website (www.stateoig.gov/hotline) or by calling (202) 647-3320 or (800) 409-9926.
g. In accordance with section 7(b) of the Inspector General Act of 1978, as amended, the OIG shall not, after receipt of a complaint or information from an employee, disclose the identity of the employee, without the consent of the employee unless the Inspector General determines such disclosure is required by law, or is unavoidable during the course of the investigation, which also includes any audit, inspection, review, or evaluation concerning the complaint or information.
h. Any individual who knowingly and willfully gives false or misleading information to OIG could be subject to criminal prosecution and/or disciplinary action, up to and including removal. Department policy in 3 FAM 4377 (42 and 45), 3 FAM 4546 (42 and 45), and 3 FAM 7724 (10 and 11) states that employees may face disciplinary action for misrepresentation, falsification, or willful omission of material fact in connection with investigations or refusal to cooperate in any authorized inquiry or investigation. Contractor and grantee employees have an obligation to provide information when requested and to answer questions from OIG officials or contractors working on behalf of OIG truthfully and completely. Contractor or grantee employees who knowingly and willfully give false or misleading information could be subject to criminal prosecution and/or suspension or debarment from involvement in government contracts and grants.
i. All individuals subject to the requirements of this section shall take an oath or give an affirmation or affidavit upon request by OIG personnel.
j. If OIG personnel interview an employee who is a member of the bargaining unit on a matter that the employee reasonably believes will result in disciplinary action against the employee, the employee may, upon request, have a union representative present. However, the employee is required to furnish pertinent information and answer all relevant questions truthfully and completely. Refusal to provide such information may be grounds for disciplinary action, up to and including removal.
k. An employee who has authority to take, direct others to take, recommend, or approve any personnel action, is prohibited from taking or threatening to take any action against any employee as a reprisal for making a complaint or disclosing information to OIG, unless the complaint was made or the information was disclosed with the knowledge that it was false or with willful disregard for its truth or falsity. If the individual is a U.S. citizen employee this prohibited personnel practice is punishable by disciplinary action, up to and including removal or civil fine (see 5 U.S.C. 2302(b)(8)).
1 FAM 053.2-3 The Head of a Bureau, Post, or Other Office of the Department of State
(CT:ORG-706; 08-15-2025)
a. Section 209(c)(6) of the Foreign Service Act of 1980 (22 U.S.C. 3929(c)(6)) requires the head of a bureau, post, or other office of the Department to submit a report to the Inspector General, within 5 business days of being made aware of any allegation of:
(1) Waste, fraud, or abuse in a Department program or operation;
(2) Serious misconduct on the part of a Department employee at the FS–1, GS–15, or GM–15 level or higher;
(3) Criminal misconduct on the part of a Department employee, regardless of position or rank; and
(4) Serious, noncriminal misconduct on the part of any Department employee who is authorized to carry a weapon, make arrests, or conduct searches, such as conduct that, if proved, would constitute perjury or material dishonesty, warrant suspension as discipline for a first offense, or result in loss of law enforcement authority.
b. Any allegation meeting the criteria reflected in paragraph a above should immediately be brought to the attention of the relevant head of a bureau, post, or bureau-level office.
c. Questions regarding this reporting requirement may be directed to the Office of the Legal Adviser for Management (L/M).
d. Intentionally delaying or attempting to prevent reporting by a Department employee or entity of this information to the appropriate head of a bureau, post, or other office may result in potential criminal prosecution and/or administrative action.
e. As outlined in 1 FAM 053.2-2, any Department employee or other personnel may also raise any allegations directly to OIG, via the OIG Hotline website.
f. For the purposes of this section, "serious misconduct" is defined as behavior or actions by a federal employee that violate established rules, regulations, policies, or standards of conduct. This would include behavior or actions which would warrant suspension as discipline for a first offense. Examples of serious misconduct include, but are not limited to: misuse of government property, falsification of records, and violations of the standards of ethical conduct. For the purposes of this section, "serious misconduct” does not include sexual or discriminatory harassment allegations, which should be reported to S/OCR.
g. For the purposes of this section, "head of a bureau, post, or other office of the Department" is hereby defined as follows:
(1) For domestic offices, the corresponding Assistant Secretary or equivalent responsible for the office involved; and
(2) For overseas offices, the Chief of Mission or equivalent responsible for the office involved.
NOTE: In either of the above cases, the responsible officer may assign another officer within their chain of command to perform the administrative tasks associated with the reporting of allegations referred to in this section.
h. Reporting under the Authorities Act should be in the form of an email to internalhotline@stateoig.gov with the subject line "Authorities Act: Report of Alleged .... ". The email should thoroughly describe the allegations and provide a point of contact for additional information.
1 FAM 053.2-4 Joint Investigations and Deconflicting Investigative Issues With the Bureau of Diplomatic Security
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
a. Section 103 of the Omnibus Diplomatic Security and Anti-terrorism Act, Public Law 99-399 (22 U.S.C. 4801, et seq.) and the Section 37 of the State Basic Authorities Act of 1956, Public Law 99-93 (22 U.S.C. 2709) established the authorities and responsibilities of the Diplomatic Security Service (DSS) (see 12 FAM). Because OIG has broad investigative jurisdiction over the programs and operations of the Department, there may be times when both DSS and OIG have investigative jurisdiction over a criminal, civil, or administrative violation.
b. As an independent law enforcement agency, OIG is not required to adhere to Department regulations governing Foreign Service and Civil Service federal law enforcement officers of the DSS. OIG falls under the authorities identified in 1 FAM 051.1. As with other personnel under COM security responsibility, OIG personnel are required to follow post-specific policies when on official duty overseas.
c. OIG may coordinate directly with domestic and international entities, including law enforcement and prosecutorial authorities, during the conduct of OIG investigative activities and law enforcement operations.
d. In instances where OIG and DSS share statutory authority over investigations, OIG special agents may coordinate directly with the appropriate DSS official (e.g., Regional Security Office (RSO), Bureau of Diplomatic Security, Criminal Investigations Division (DS/ICI/CR), Overseas Criminal Investigations Division (DS/ICI/OCI), or Office of Special Investigations (DS/DO/OSI)) to determine if a joint investigation is warranted.
e. Any issues that cannot be resolved between DSS and OIG special agents will be elevated to the Deputy Assistant Inspector General for Investigations and the appropriate DSS Deputy Assistant Secretary for resolution.
1 FAM 053.3 Impasse Resolution
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
An OIG recommendation is a statement in an OIG report requiring action by the addressee organizations or officials to correct a deficiency or need for change or improvement identified in the report. When the action office makes no response to an OIG recommendation, rejects it, or does not resolve it after a reasonable effort to achieve agreement, the OIG may take the issue to impasse.
1 FAM 053.3-1 Under Secretary for Management
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
The Under Secretary for Management (M) is the Secretary’s designated top management official responsible for audit and inspection follow-up and the Secretary’s designee for impasse resolution when Department officials do not agree with OIG recommendations for corrective action unless the action office reports to M. Should the action office report to M, then the Executive Secretary for the Secretary of State will assign as the impasse official a separate Under Secretary.
1 FAM 053.3-2 Chief Executive Officer of the U.S. Agency for Global Media
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023
The CEO or a designee is the top management official responsible for audit and inspection follow-up and the designee for impasse resolution when USAGM officials do not agree with OIG recommendations for corrective action.
1 FAM 053.3-3 United States Commissioner of the International Boundary and Water Commission, United States and Mexico, U.S. Section
(CT:ORG-623; 04-06-2023)
Unless otherwise specified in writing, the Commissioner is considered the top management official responsible for audit and inspection follow-up and the designee for impasse resolution when USIBWC officials do not agree with OIG recommendations for corrective action.
1 FAM Exhibit 050(1)
List of Acronyms
(CT:ORG-655; 03-29-2024)
|
CIGIE |
Council of the Inspectors General on Integrity and Efficiency |
|
COM |
Chief of Mission |
|
Department |
U.S. Department of State |
|
DS |
Bureau of Diplomatic Security |
|
DSS |
Diplomatic Security Service |
|
FOIA |
Freedom of Information Act |
|
GAGAS |
Generally Accepted Government Auditing Standards |
|
GAO |
Government Accountability Office |
|
L/EMP |
Office of the Legal Adviser for Employment Law |
|
OIG |
Office of Inspector General |
|
OIG/AUD |
Office of Audits |
|
OIG/CPA |
Office of Congressional and Public Affairs |
|
OIG/ERM |
Office of Enterprise Risk Management |
|
OIG/ESP |
Office of Evaluations and Special Projects |
|
OIG/EX |
Office of the Executive Director |
|
OIG/INV |
Office of Investigations |
|
OIG/ISP |
Office of Inspections |
|
OIG/GEER |
Global Emergencies and Emerging Risks Division |
|
OIG/OGC |
Office of General Counsel |
|
OIG/OCO |
Office of Overseas Contingency Operations |
|
PA |
Privacy Act |
|
SAR |
Semiannual Report to the Congress |
|
Secretary |
Secretary of State |
|
USAGM |
U.S. Agency for Global Media |
|
USIBWC |
International Boundary and Water Commission, United States and Mexico, U.S. Section |
1 FAM Exhibit 050(2)
Organizational Chart
(CT:ORG-655; 03-29-2024)