Bureau of Budget and Planning (BP)
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
(Office of Origin: CGFS/EX)
1 FAM 621 director OF Budget and Planning (BP)
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
The Director of Budget and Planning heads the Bureau of Budget and Planning (BP) and reports to the Under Secretary for Management.
1 FAM 621.1 Director Responsibilities
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
The Director of BP:
(1) Projects, acquires, and allocates the appropriated and reimbursed resources necessary for the Department to conduct diplomatic and consular relations to achieve U.S. foreign policy objectives;
(2) Directs the planning, development, and conduct of the Department's integrated planning, performance, and budget processes;
(3) Prepares budget requests and performance information for consideration by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the Congress;
(4) Issues financial allotments, which provide actual resources to the various bureaus and offices of the Department;
(5) Assures consistency with Presidential priorities and legislative mandates through resource allocations and utilization, and through execution of the Department's budget;
(6) Supports drafting of Secretarial and other senior officials statements and testimony related to resource requests;
(7) Meets with and addresses external constituents, Chiefs of Mission, and senior officials of other agencies on Diplomatic Engagement resource, planning, and performance issues;
(8) Proposes and reviews legislative strategies for acquiring and maintaining an appropriate level of resources for the Department;
(9) Serves as a principal or supporting witness at OMB and Congressional hearings on Department budget and management matters;
(10) Develops programmatic performance information for inclusion in budget and performance systems and reports;
(11) Directs the development of the Diplomatic Engagement Strategic Planning Process; reviews bureau process and provides leadership on the Department Strategic goals and accomplishments;
(12) Oversees the preparation and issuance of the Diplomatic Engagement Strategic Plan, Annual Performance Report, and the annual Performance Plan;
(13) Monitors the Department of State’s operational program evaluations and ensuring the recommendations are incorporated in program improvement plans;
(14) Ensures budgetary and performance systems produce useful, reliable, and timely information; and
(15) Prepares budget and performance guidance for issuance in the Foreign Affairs Manual or Foreign Affairs Handbook.
(16) Serves as the Department's Performance Improvement Officer in accordance with the Government Performance and Results Modernization Act.
1 FAM 621.2 Bureau Responsibilities
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
The Bureau of Budget and Planning:
(1) Coordinates requests to enable the Secretary of State to present integrated international affairs resource submission to OMB and to the Congress;
(2) Promotes foreign policy objectives:
(a) By assisting foreign affairs agency heads in developing policies, plans and programs to achieve foreign policy goals;
(b) By supporting the Department's strategic and performance planning; and
(c) By obtaining and allocating funds for the Department's operations;
(3) Plans, develops, presents, justifies, and defends legislative proposals of the Department that relate to Department appropriations, trust funds, and other accounts falling under Department operations;
(4) Participates in the Department program planning to facilitate estimation of resource needs to achieve policy goals and objectives;
(5) Develops and implements strategies for the most effective and persuasive presentation of the Department's budget proposals for consideration by OMB, the President, and the Congress;
(6) Allocates Department resources consistent with Department policies and objectives, and applicable laws and regulations;
(7) Manages the review and evaluation of all enacted legislation relative to the Department to determine resource implications and effects on execution of program objectives;
(8) Ensures efficient and effective use of Department resources and analyzes and evaluates their use in accomplishing Department program objectives;
(9) Analyzes budget requirements and expenditure trends in relation to overall Department mission and specific bureau and office functions;
(10)Oversees the development of internal Department budgetary systems and ensures interoperability as business owner for Department budgetary systems;
(11)Oversees the Department’s strategic and performance planning activities and provides policy, planning and analytical support to all bureaus and missions;
(12)Develops, in coordination with the Office of Foreign Assistance Resources (F), the joint State-USAID Strategic Plan, the Department’s Performance Plan, Performance and Accountability Report, and post- and bureau-level strategic plans and processes;
(13)Oversees the Department’s compliance with the Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) of 1993 and the GPRA Modernization Act of 2010 (GPRAMA), the Program Management Improvement Accountability Act (PMIAA) of 2016 and the Foundations for Evidence-Based Policymaking Act (Evidence Act) of 2018;
(14)Manages, with F, planning and performance issues;
(15)Coordinates with F on the annual senior policy, performance, and resource reviews of bureaus’ planning and budget requirements for the Department;
(16)Oversees the following offices:
(a) Office of Resource Planning and Budget Information (BP/RPBI);
(b) Office of Budget Analysis (BP/OBA); and
(c) Office of Performance and Planning (BP/OPP);
(17)Directs the development of strategic planning and policy formulation processes linked to resource acquisition and management;
(18)Assists international affairs (Function 150) agency heads in developing policies, plans, and programs to achieve U.S. foreign policy goals;
(19)Reviews major legislative and other programmatic proposals and provides advice to the Secretary on Federal cost and program benefit estimates (major procurements and changes in credit programs);
(20) Mandates Department-wide data and reporting format requirements for budget systems; and
(23) Represents the Department on the U.S. government-wide Budget Officers Advisory Council (BOAC), and the Performance Improvement Council.
1 FAM 621.3 Organization
(CT:ORG-291; 11-14-2012)
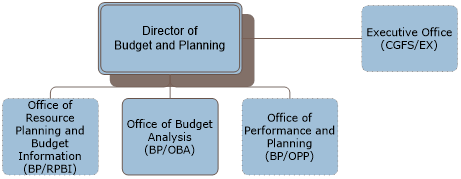
See 1 FAM Exhibit 621.3 for an organization chart of the Bureau of Budget and Planning (BP).
1 FAM 621.4 Authorities
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
Legal authorities pertaining to the work of BP include:
(1) Annual Department of State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs Appropriations Act—This is an annual appropriation;
(2) Clinger-Cohen Act (Information Technology Management Reform Act) (Division E of Public Law 104-106);
(3) Foreign Relations Authorizations Acts—This legislation is usually enacted every two years;
(4) Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) of 1993 (31 U.S.C. 1115 and 31 U.S.C. 1116; Public Law 103-62);
(5) GPRA Modernization Act of 2010 (31 U.S.C. 1101, Public Law 111-352);
(6) Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995 (Public Law 104-13);
(7) State Department Basic Authorities Act (BAA) of 1956, as amended (22 U.S.C. 2651a et. seq.)—Establishes the organizational structure of the Department and provides many of its management authorities;
(8) Other significant external authorities pertaining to the work of BP include circulars and other guidance from the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), and Department of Treasury guidance.
(9) Digital Accountability and Transparency Act (DATA ACT) of 2014;
(10) The Good Accounting Obligation in Government Act (Public Law 115-414);
(11) Program Management Improvement Accountability Act (PMIAA) of 2016 (Public Law 114-264); and
(12) Foundations for Evidence-Based Policymaking Act (Evidence Act) of 2018 (Public Law 115-435).
1 FAM 621.5 Definitions
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
For purposes of this FAM, the following definitions are provided:
Allotment: Once apportionment authority is received by the Department, it is made available through “allotments” issued by BP to the respective bureaus. Allotment Authorities are issued at the highest aggregate funding level to major bureaus (e.g., geographic regional bureaus, Bureau of Administration, Bureau of Diplomatic Security) anticipating the resources will be divided further among posts or multiple activities or programs. The subdivision of funds is accomplished by a bureau issuing advices of allotment to posts or activities/programs. BP itself also issues Advices of Allotment to smaller domestic bureaus that do not have an obvious need to subdivide the resources. Nevertheless, Advices of Allotment may in turn be further subdivided into Operating Allowances issued to constituent posts/programs. Both Allotment Authorities and Advices of Allotment conform to apportioned distributions and provide bureaus funds to conduct activities and make obligations not to exceed the values stated. Allotted amounts represent decisions made by the Under Secretary for Management or other designated senior Department officials in approving financial operating plans. (Also see 4 FAH-3 H-122.2)
Agency Financial Report (AFR): A report on the agency end of fiscal year financial position that includes, but is not limited to, financial statements, notes to the financial statements, and a report of the independent auditors. The report also includes a performance summary that, when combined with the Annual Performance Report, meets the requirements for submitting the consolidated Performance and Accountability Report. This report is currently published jointly with the APP.
Annual Performance Plan (APP): Under the GPRA Modernization Act (31 U.S.C. 1115 et seq), an agency’s Annual Performance Plan covers each program activity set forth in the budget, identifying the agency’s goals and objectives and how those goals will be achieved. The APP links performance goals with resources for achieving a target level of performance on an annual basis. An Annual Performance Plan aligns activities under the agency’s strategic goals, showing budget information for specific activities intended to influence outcomes. This report is currently published jointly with the AFR.
Annual Performance Report (APR): A report on agency performance that is delivered with an agency’s Congressional Budget Justification to Congress every February. The APR contains information on the agency’s progress to achieve goals during the past year as set forth in the APP.
Apportionment: An apportionment is a plan, approved by OMB, to spend resources provided by any of the following: one of the annual appropriations acts, a supplemental appropriations act, a continuing resolution, or a permanent law (i.e., mandatory appropriations). Resources are apportioned by Treasury Appropriation Fund Symbol (TAFS). The apportionment identifies amounts available for obligation and expenditure. It specifies and limits the obligations that may be incurred and expenditures made (or makes other limitations, as appropriate) for specified time periods, programs, activities, projects, objects, or any combination thereof. An apportioned amount may be further subdivided by an agency into allotments, sub-allotments, and allocations.
Appropriation Conference: A bicameral committee of the House and Senate committees on Appropriations, that generally provides budget authority for federal agencies including the Department of State to incur obligations and to make certain payments out of the Treasury for specified purposes in accordance with requirements of Article I, Section 9, of the United States Constitution.
Budget Authority: Authority provided by federal law to enter into financial obligations that will result in outlays involving federal government funds. Per OMB Circular A-11, budget authority includes: (1) appropriations; (2) borrowing authority; (3) contract authority; and (4) authority to obligate and expend offsetting receipts and collections.
Congressional Budget Justification (CBJ) and Associated Appendices: In accordance with the Budget and Accounting Act of 1921 (31 U.S.C. 1105), the Department prepares and submits an annual budget request for Diplomatic Engagement, an annual budgetary resource request summary of Function 150 and other international programs, detailing the funding requested to support budgetary policy priorities of people, security, facilities, information technology, and management reforms.
Congressional Notification: A specific requirement as prescribed by law for the Department to provide congressional committees programming and activity information prior to or in conjunction with action.
Evaluation: Individual, systematic studies to assess how well a program is working to achieve intended results or outcomes. They are often conducted by experts external to the program either inside or outside an agency. Evaluations can help policymakers and agency managers strengthen the design and operation of programs and can help determine how best to spend taxpayer dollars effectively and efficiently. Evaluations identified should be performed with appropriate scope, quality, and independence.
Financial Plan (FINPLAN): The resource allocation plan as approved by the Under Secretary for Management / Chief Financial Officer and the Congress developed to provide guidance for allocation of financial resources in accordance with enacted appropriation legislation and Departmental priorities.
Financial Plan Review: The periodic review of resource allocations, obligations and expenditures, and program performance to determine unfunded requirements not previously identified. Financial Plan reviews are performed on an as need basis.
Functional Bureau Strategies (FBS): A focused, subject matter specific strategic plan developed by each functional bureau that sets priorities and is based on coordination between the functional bureaus and partner regional bureaus, key overseas missions, and interagency partners. The FBS is used to inform budget decisions, advise integrated country strategies, and shape performance reviews.
Integrated Country Strategies (ICS): The strategic plan developed by each mission overseas that serves as a single multi-year overarching strategy that encapsulates U.S. government policy priorities, objectives, and the means by which diplomatic engagement, foreign assistance, and other tools will be used to achieve them. The ICS is developed through a coordinated whole-of-government planning effort and is used to inform budget decisions, drive operational planning decisions, and shape performance reviews.
Internal control: The steps taken to provide reasonable assurance that obligations and costs are in compliance with applicable law; funds, property, and other assets are safeguarded; revenues and expenditures applicable to Departmental operations are properly recorded and accounted for; and programs are efficiently and effectively carried out in accordance with law and management policy.
Intra-governmental Payment and Collection (IPAC): A system that allows agencies to issue payments and provide collecting capabilities by going through the Department of Treasury via the Internet.
Joint Regional Strategies (JRS): An integrated strategic plan developed jointly between the State and USAID Regional Bureaus that involves the equities of both agencies, and involves both non-regional bureaus and interagency partners with a stake in the region. The JRS is used to inform budget decisions, advise integrated country strategies, and shape performance reviews.
Joint State/USAID Strategic Plan (JSP): Strategic planning and performance management are guided by the Quadrennial Diplomacy and Development Review (QDDR) and the GPRA Modernization Act of 2010. The QDDR serves as the new State-USAID Joint Strategic Plan (JSP), and sets institutional priorities and provides strategic guidance as a framework for the most efficient allocation of resources. The QDDR also includes directives for improving how posts do business, from strengthening interagency collaboration to increasing State and USAID engagement with civil society, the private sector and others.
Mark-Up: The process by which congressional committees debate, amend, and rewrite proposed appropriation and authorization legislations.
Reprogramming: Shifting funds within an appropriation or fund account to use them for purposes other than those contemplated at the time of appropriation. Appropriations acts cite specific requirements or reprogramming thresholds which require a congressional notification.
Transfer: A transfer is a non-expenditure shift of budgetary authority from one organizational element to another. Internal transfers often happen between two organizational entities within the same fund. External transfers or expenditure transfers processed by Treasury and require apportionment actions approved by OMB.
Warrant: An official document issued by the Secretary of the Treasury that reflects an amount of money authorized and appropriated by public law to be withdrawn from the Department of Treasury. Warranted amounts are established in Treasury Department accounts and subsequent fiscal activity reported by administering departments and agencies is reflected against those amounts for consolidated Federal accounting.
Working Capital Fund (WCF): A no-year fund that permits unobligated money to be carried over from one fiscal year to the next, providing fiscal flexibility. Funds may be authorized for expenses and equipment necessary for maintenance and operation in Washington, DC and elsewhere. These include centralized services for reproduction, editorial, data processing, audiovisual, library, and administrative support services; supplies and equipment; and other administrative services the Secretary determines may be performed more advantageously and more economically as central services (with OMB approval).
1 FAM 622 Budget Planning Offices
(CT:ORG-291; 11-14-2012)
a. The Bureau of Budget and Planning (BP) consists of the following offices:
(1) Office of Resource Planning and Budget Information (BP/RPBI);
(2) Office of Budget Analysis (BP/OBA);
(3) Office of Performance and Planning (BP/OPP);
b. The Executive Director for CGFS (CGFS/EX) supports both BP and CGFS. See 1 FAM 610 for the services provided to BP by CGFS/EX.
1 FAM 622.1 Office of Resource Planning and Budget Information (BP/RPBI)
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
The Office of Resource Planning and Budget Information (BP/RPBI) is headed by a Deputy Assistant Secretary (DAS) equivalent Deputy Director. This office:
(1) Plans, develops, justifies, presents, and defends the legislative proposals of the Department for all Diplomatic Engagement appropriations, trust funds, and other accounts; ensures understanding of costs associated with legislative proposals and appropriations legislation;
(2) Establishes long range and integrated Department resource planning strategies that reflect Administration and Department priorities and interagency coordination, within the context of the Department's overall planning and budgeting functions;
(3) Creates and articulates the Department's overall budget strategy for incorporation in the Congressional Budget Justification, principals’ speeches on resource issues, and public outreach strategy papers on Department resources;
(4) Tracks and tasks the preparation of responses to Congressional mandates and inquiries, as well as distributing this information as appropriate;
(5) Ensures that BP systems produce relevant, timely, and coherent information and reports that enhance analysis and understanding of Department of State funding requirements and budget execution;
(6) Directs operational funds-control activities that ensure that the Department is exercising its fiduciary responsibilities in compliance with law and regulation, including:
(a) Obtaining spending warrant authorities from the Treasury Department (including OMB clearance when required); and
(b) Coordinating and controlling transactions concerning movement of funds at the appropriation level to and from other U.S. Government agencies through the Treasury Department.
(7) Transmits budgetary and resource availability data to the Treasury Department via proprietary online systems;
(8) Develops and obtains apportionment of funds from OMB;
(9) Maintains and enhances the Department's centralized budget formulation, execution, and funds control system through the establishment of appropriation and other internal controls and issuance of legally binding allotment documents to bureau principals for all Department appropriations;
(10) Develops and negotiates or advises on reimbursement agreements with U.S. Government agencies receiving support from the Department to achieve full recovery of the value of services provided; provides data documentation and other support regarding reimbursable earnings to accommodate accounts receivable to ensure collection of earned income;
(11) Conducts special studies of budgetary practices or reporting issues to identify and implement improvements in or innovative approaches to budgeting and reporting; participates on task forces or similar groups that develop recommendations concerning government-wide budgeting practices; and
(12) Provides and maintains historical and current budget backup materials, baseline historical data, prior-year budget, and historical budget execution data.
(13) Works to mitigate the Department's exposure to related vulnerabilities and threats in particular involving cyber and physical infrastructure.
1 FAM 622.2 Office of Budget Analysis (BP/OBA)
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
The Office of Budget Analysis (BP/OBA) is headed by a Deputy Assistant Secretary (DAS) equivalent Deputy Director. This office:
(1) Improves overall financial management and maximization of Department resources;
(2) Develops and implements resources management processes and proposals for Department's Diplomatic Engagement accounts;
(3) Develops and implements special studies on resource issues, addressing short and long-term strategic factors, resource utilization, policy and operating requirements, and other factors, and develops solutions or approaches to these issues;
(4) Recommends presentation strategies for all accounts;
(5) Reviews bureau and program requirements in light of foreign policy objectives, economic factors and administration policies, and makes recommendations to M and other Department principals on resource levels;
(6) Works in coordination with RBPI to develop appropriations language concerning those resources requested for each serviced bureau and Diplomatic Engagement account included in the Department's budget request;
(7) Assists bureaus in the development of annual financial plans; analyzes financial plans submitted by bureaus and offices, develops a financial plan for the entire Department, monitors the execution of approved financial plans, and recommends the reprogramming of resource reallocations;
(8) Advises on intelligence issues affecting the budgetary interests of the Department; coordinates with the intelligence community and analyzes current and prospective intelligence resource matters; represents the Department’s resource interests on planning committees or similar groups; coordinates to ensure that the Department’s budget priorities are appropriately known;
(9) Conducts periodic reviews on the status of all operating accounts, including monitoring financial and program performance against bureau objectives and highlighting findings and making mid-course recommendations;
(10) In conjunction with CGFS, prepares and justifies budget requests for the centrally managed Foreign Service Retirement and Disability Fund and the Foreign Service Pension System Fund;
(11) Performs analysis of the effect of foreign currency fluctuations with particular emphasis on the effect on the Buying Power Maintenance Account;
(12) Manages and controls the funds allotted for the Department's centralized U.S. salaries account. The division prepares and justifies budget requests for full-time permanent U.S. citizen salaries for consideration by OMB and the Congress and develops special analyses relating to the effect of alternative staff and benefit levels on U.S. citizen salary requirements;
(13) Plans, develops, and implements cross-cutting analyses of domestic and international Department salaries, prices, and base operations; and
(14) Develops and presents special analyses relating to resource use and projected needs requested by senior Department management, Congress, and the Congressional Budget Office.
1 FAM 622.3 Office of Performance and Planning (BP/OPP)
(CT:ORG-540; 12-20-2019)
The Office of Performance and Planning (BP/OPP) is headed by a Managing Director. This office:
(1) In coordination with F, oversees the Department’s annual performance planning and reporting processes, systems, and products that comply with the Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) and support the Administration’s initiatives on performance;
(2) Works to integrate strategic planning and key performance information into analysis and preparation of budget requests for the Diplomatic Engagement accounts;
(3) Evaluates bureau resource investments to ensure alignment with Department performance goals and initiatives;
(4) Provides analysis on strategic planning and performance for policymakers and others;
(5) Briefs senior policymakers and bureau planners about progress in implementing strategic planning and performance policy;
(6) Organizes and provides analysis for the review of Integrated Country Strategies by BP and the regional bureaus as well for the bureau strategic plans by the Department’s senior leadership;
(7) Develops and manages the budgetary content of Department of State strategic plans, performance plans, bureau performance plans, and mission performance plans;
(8) Manages performance reporting by the Department to OMB;
(9) In conjunction with F, oversees the implementation of the Department’s evaluation policy; and
(10) Establishes performance measures that ensure Department plans, budget requests, and actual appropriation and execution results meet the requirements of OMB Circulars A-11 and A-136, GPRA and the GPRA Modernization Act of 2010, CFO’s Act and Federal Manager's Financial Integrity Act of 1982 (FMFIA), as well as annual appropriations legislation.
(11) Serves as the Deputy Performance Improvement Officer in accordance with the Government Performance Results Modernization Act.
1 FAM 623 through 629 unassigned
1 FAM EXHIBIT 621.3
BUREAU OF BUDGET AND PLANNING
(CT:ORG-291; 11-14-2012)